Integral surgical and orthodontic treatment of an autotransplanted maxillary canine: case report
Introduction: The main treatment of impacted canines is orthodontics. In case of failure, extraction of the canine and the subsequent placement of a dental implant is given as an alternative. Autotransplantation is considered a treatment option as long as the full extraction of the canine is viable, because it provides many advantages as the ability of mobilization with orthodontics
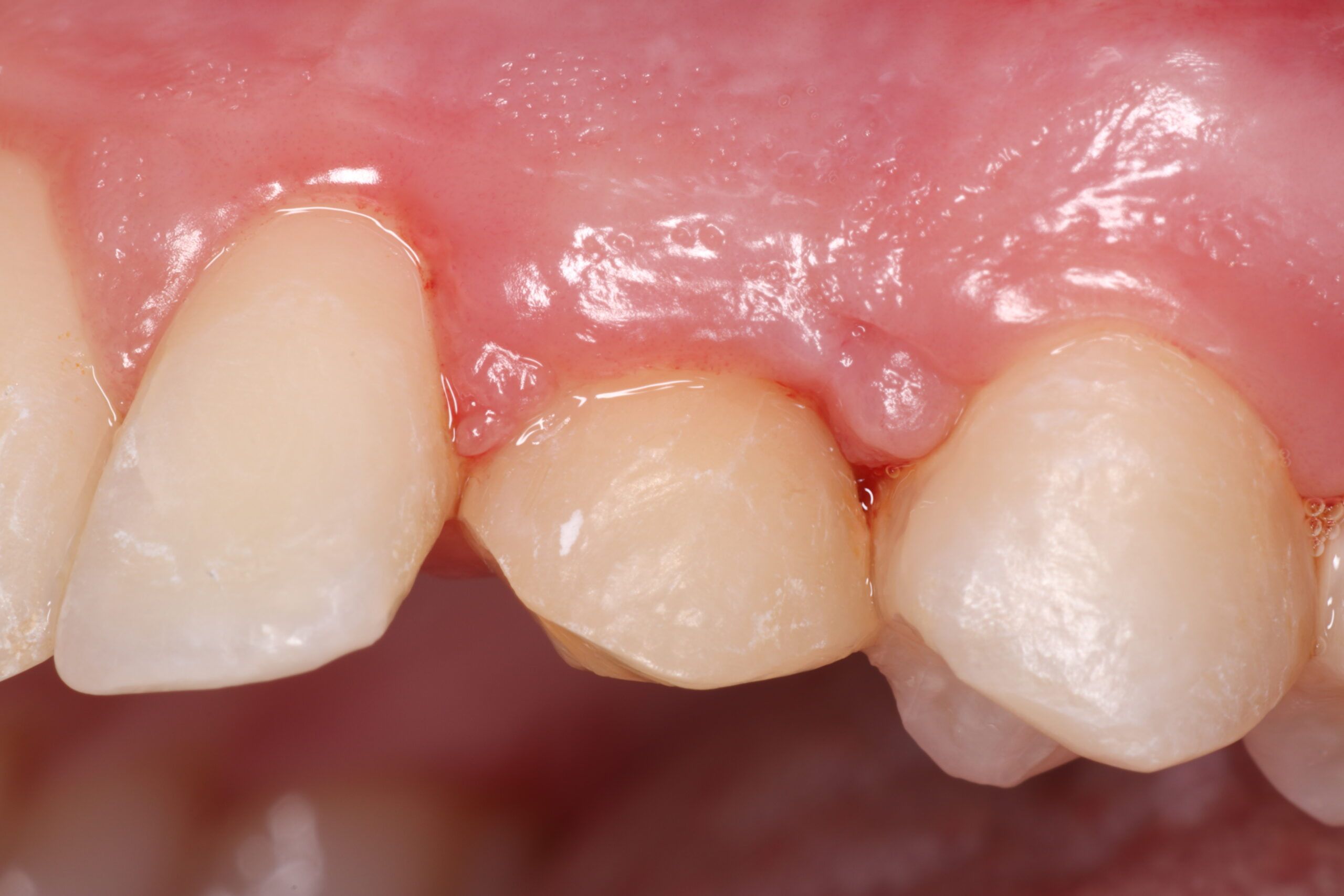
Case report: Description of a clinical case in which an autotransplantation of an included canine was carried out after traction failed in a young patient. After regenerative surgery was realized in its surroundings the patient underwent orthodontic and restorative treatment. 18 months of follow–up later the patient remains asymptomatic, with no mobility or resorption signs and with a healthy periodontal state in said canine.
Conclusion: Autotransplantation can be a suitable alternative when orthodontic traction has failed, as long as it is viable, especially in young patients when implants are not recommended.